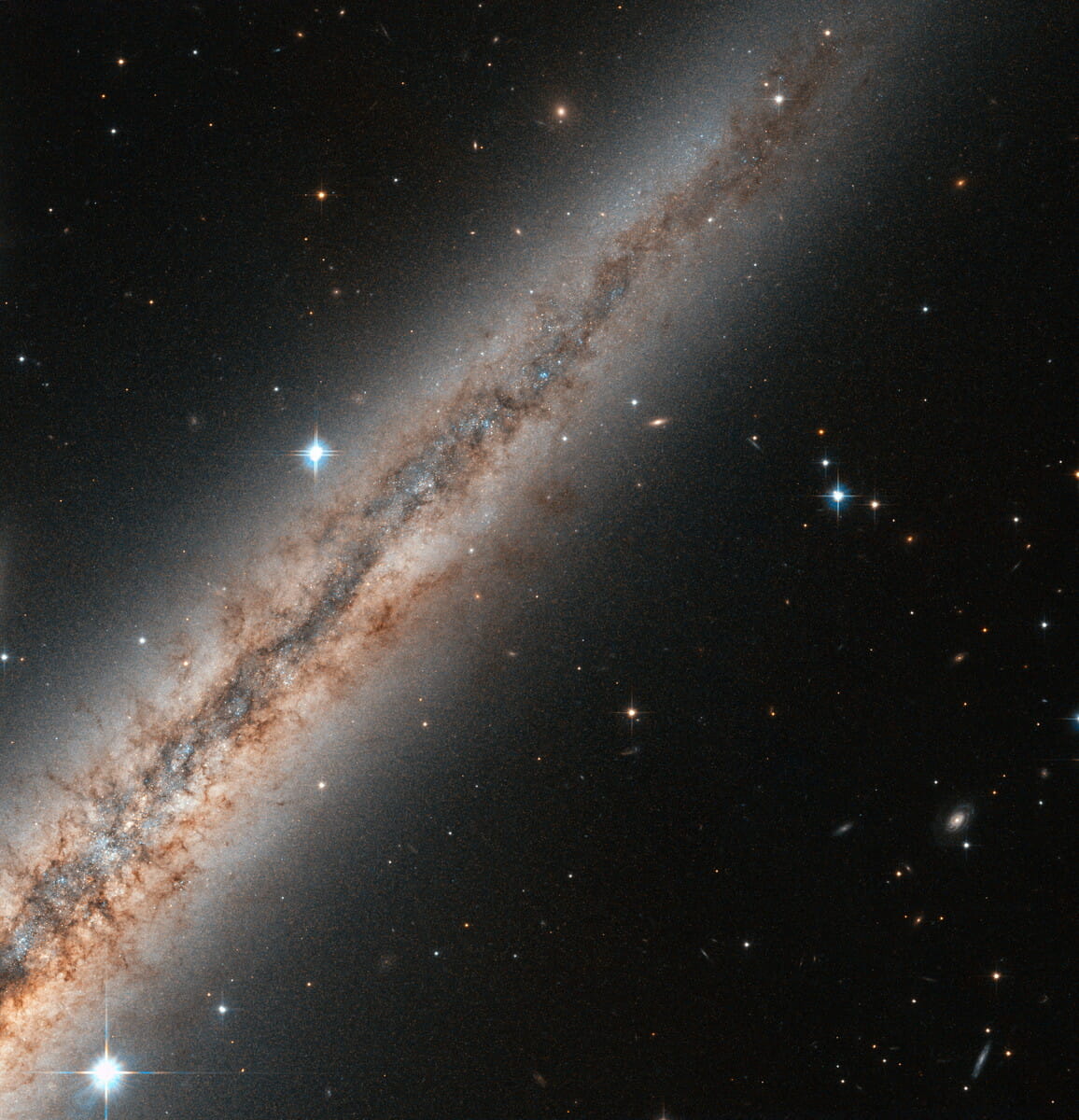
夜空に輝く天の川を撮影したようにも思えるこちらの画像、帯のように集まっているのは私たちが住む天の川銀河の星々ではなく、別の銀河の星々から届いた光。これはアンドロメダ座の方向およそ3500万光年先にある銀河「NGC 891」の一部を捉えた画像です。
全体が写っている下の画像を見るとわかるように、NGC 891は地球に対して真横を向けた位置関係にある、いわゆるエッジオン銀河のひとつです。NGC 891は銀河円盤の幅が天の川銀河と同じ約10万光年の渦巻銀河とされていますが、横から見ているために特徴的な渦巻腕を観察することはできません。その姿は、宇宙に生じた裂け目のようだと表現されることもあります。
そんなNGC 891では、銀河を取り囲む希薄なハローへと流れ出ていくガスや塵でできた、数百光年規模のフィラメント構造が観測されています。銀河円盤からガスや塵が流出しているのは、活発な星形成活動によって形成された星々の恒星風や超新星爆発によって吹き飛ばされたためと考えられています。
なお、NGC 891はイギリスのアマチュア天文家サー・パトリック・ムーア氏によって1980年代にまとめられたアマチュア天文家向けの天体カタログ「Caldwell Catalog」(カルドウェルカタログ、またはコールドウェルカタログ)に「Caldwell 23」として登録されています。冒頭の画像は「ハッブル」宇宙望遠鏡の「掃天観測用高性能カメラ(ACS)」によって可視光線と赤外線の波長で観測されたものです。
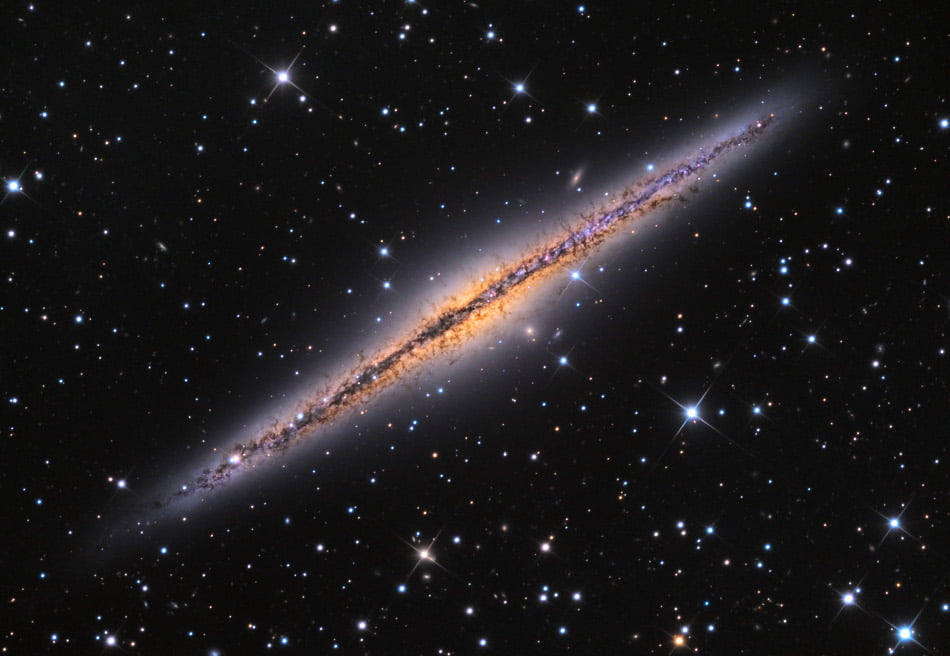

Image Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA
Source: ESA/Hubble / NASA / APOD
文/松村武宏